Overview
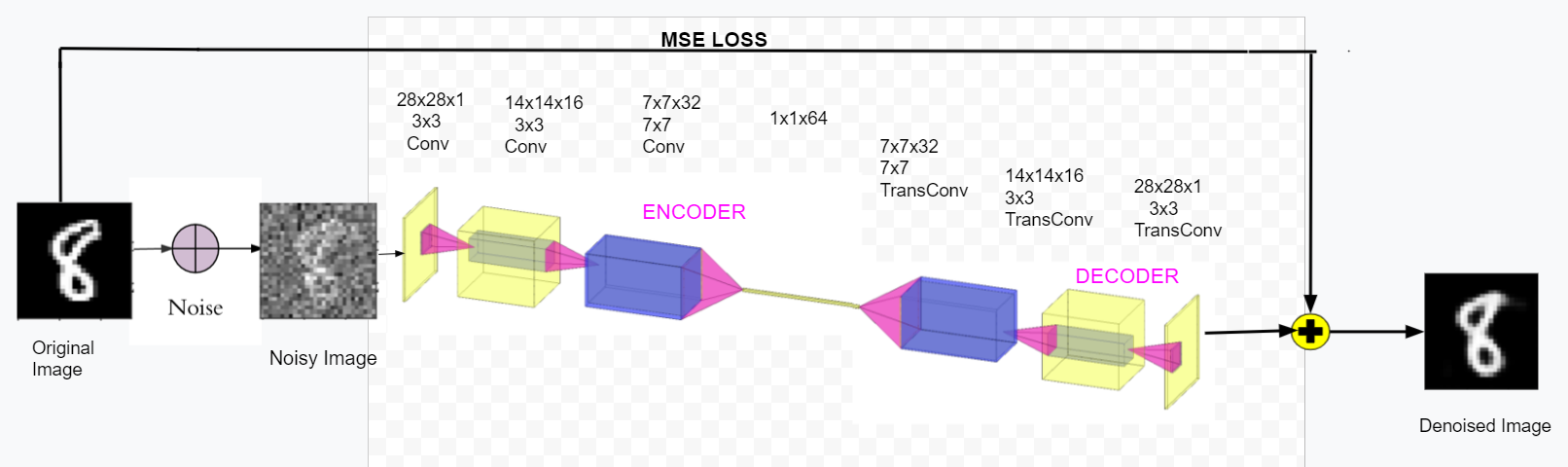
This project involved implementing an Image Denoising model, specifically a Vanilla Autoencoder on the MNIST dataset. In the Denoising Autoencoder framework, we introduce noise to the input images, using a random function with a tunable parameter. The encoder compresses this noisy input into a lower-dimensional latent space, capturing essential patterns. The decoder then reconstructs the original image from this compressed representation. The reconstruction error is minimised using Mean Squared Error (MSE) loss between the original and reconstructed images. The loss is backpropagated to update the model parameters using the Adam optimizer, to improve the model’s ability to denoise and reconstruct the input images.
The model architecture follows a typical autoencoder structure, and is similar to the one depicted here.
MNIST Dataset
The MNIST Dataset consists of 60000 training samples and 10000 test samples of a handwritten digit between 0 and 9. Each sample is a 28 x 28 grayscale image of the digit.

Parameters and Loss Plots
| HyperParameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Batch Size | 32 |
| Learning Rate | 0.001 |
| Number of Epochs | 10 |
| Loss Function | MSE Loss |
| Optimizer | Adam Optimizer |
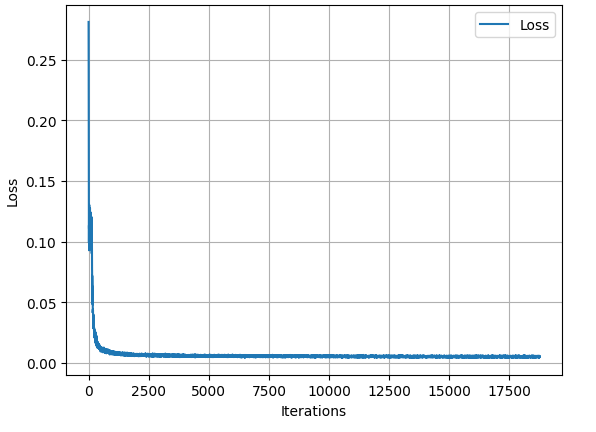
The variation of loss over all iterations is shown in this figure.
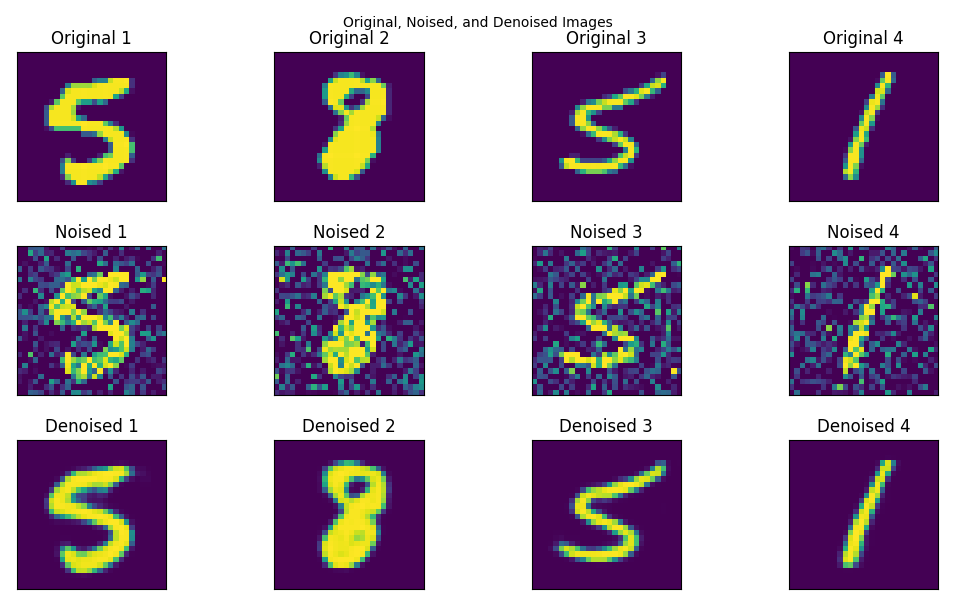
Results
Related Work
During my study of Neural Networks, I implemented two MNIST classifier models: one using PyTorch and the other by building a neural network from scratch using NumPy. The source code for these models can be found here.